Learning Objectives:
* Understanding the various types of data type in Python and the correct implementation of these
* A fast recap over the data type 'dictionary' and how is it different from the other data types
* How to create a pandas series through an existing dictionary
* Understanding the purpose of various attributes and methods of the Construct Series( )
Text highlighted in blue colour to be pen down in the IP register along with the code.
Certain points/terms which should be clear before we start
Dictionary - a set of key: value pairs, with the requirement that the keys are unique (within one dictionary).
{} |
 |
pop() method removes the item with the specified key name:popitem() method removes the last inserted item (in versions before 3.7, a random item is del keyword removes the item with the specified key name:del keyword can also delete the dictionary completely:Python has a set of built-in methods that you can use on dictionaries.
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| clear() | Removes all the elements from the dictionary |
| copy() | Returns a copy of the dictionary |
| fromkeys() | Returns a dictionary with the specified keys and value |
| get() | Returns the value of the specified key |
| items() | Returns a list containing a tuple for each key value pair |
| keys() | Returns a list containing the dictionary's keys |
| pop() | Removes the element with the specified key |
| popitem() | Removes the last inserted key-value pair |
| setdefault() | Returns the value of the specified key. If the key does not exist: insert the key, with the specified value |
| update() | Updates the dictionary with the specified key-value pairs |
| values() | Returns a list of all the values in the dictionary |
Creating a Pandas Series from Dictionary
A Pandas Series is a labeled (indexed) array that holds data.
Series(data [, index]) - is the construct( )of the library Pandas (So import pandas to use this method). This method converts the data (dictionary here) in its arguments into a series. index allows to rearrange the order of the items.
a. Creating a pandas series using Series( data)
b. Creating a pandas series with the argument/ parameter index - this keyword may be used when the order of the key-value needs to be changed.
Features Brand Ford Model Mustang Year 1964 dtype: object
Features Brand Ford Model Mustang Year 1964 Name: It's the best, dtype: object
print(MyS.values) - ['Ford' 'Mustang' 1964]
diction2 = {
" " : "Ford",
"Model": " ",
"Year" : 1964
}
MyS=pa.Series(diction2)
print(MyS.values)
print(S1.values) - [100 200 300 400 100]
TypeError: cannot do label indexing on <class 'pandas.core.indexes.base.Index'> with these indexers [0] of <class 'int'>When the argument value of key is passed as the exact names defined in the key then will return the 'value' of the respective key.
import pandas as pd
d1={ '1':100, '2':200, '3':'Python', '4': 300.12, '5':400}
s1 = pd.Series(d1)
print("Original Data Series:")
print(s1)
print("Change the said data type to numeric:")
s2 = pd.to_numeric(s1)
print(s2)
2. sort_values( ) -
import pandas as pd
d1={ '1':600, '2':200, '3':150, '4': 300.12, '5':400}
s1 = pd.Series(d1)
print("Original Data Series:", s1)
new_s = s1.sort_values()
print(new_s)
3. abs( series_object)
Returns a Series with absolute numeric value of each element. This function only applies to elements that are all numeric.
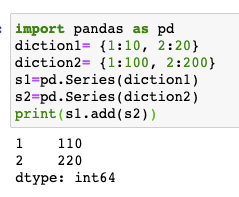
TypeError: bad operand type for abs(): 'str'4. add(series_objects[, fill_value] ) will add (mathematically)the respective matching key values of the series_objects and will show "NaN" as the value for unmatching keys.
5. agg( 'kwargs') - agg is short for aggregate and this function allows to calculate the aggregate values like minimum, maximum, average on the basis of mean and median, of the given numeric series.
6. aggregate( func='kwargs') - aggregate function allows to calculate the aggregate values like minimum, maximum, average on the basis of mean and median, of the given numeric series same as agg( ) but with a difference here the keyword 'func' is used to assign it with the desired statistical operation name.
s1.aggregate(func='sum') <--> s1.agg('sum')
**Kwargs
7. append( series_objects ) - to add two or more series one after the other.
Concatenating more than one series (Dictionary Based)
7. transform( lambda kwargs ) - to change / update the values of the series created from a dictionary by specifying the series as a user defined variable.
Lambda functions are small functions usually not more than a line. It can have any number of arguments just like a normal function. The body of lambda functions is very small and consists of only one expression.
But before this let us recall how to create a user-defined function / method
def ami(x,y):
return x+y
x = 10
y = 20
print(ami(x,y))
Output - 30
Now the same above task can also be done by lambda function -
print( (lambda x, y : x + y) (10,20) )
30
Lambda function can be used to save both coding and time.
Lambda in Series --> Lambda function can be used to update the data of series when used as kwarg to transform( ). This function will let the user defined variable be introduced immediately after its name and the update / mathematical calculation / statistical calculation will be followed by the colon.
series_object.transform( lambda variable : variable update operation )
x-x.sum( )
x.sum( ) = 100 + 90+ 100 + 90 =380
x-x.sum( ) = 100-380 = -280
import pandas as pd
diction1= {'Stud1':100, 'Stud2':98, 'Stud3':85, 'Stud4':88}
s1=pd.Series(diction1)
print(s1.transform(lambda y:y+y.sum()))
print(s1.transform(lambda x: x-x.mean()))
8. to_list( ) - to convert a series to a python list.
Output - The values of series are converted into list items and are enclosed within square bracket.
** Nested dictionary = 1 dictionary ( A series made from nested dictionary)
import pandas as pd
nd={'d1':{'Stud1':100, 'Stud2':95},
'd2':{'Stud3':95, 'Stud4':98}
}
s1= pd.Series(nd)
print("Nested Dictionary", nd)
print("One Series\n", s1)
** The individual dictionaries of a nested dictionary can have any data and of any number
When such a series(made up of a nested dictionary) is converted to a list the output list will be enclosed in angular braces but each dictionary will be enclosed within curly braces (still a dictionary).
9. apply( lambda / [(pd.Series).func( )] ) - will perform the custom / user defined operation on the elements or values of the Series (row-wise).
apply( lambda )
import pandas as pd
d1={'Stud1':100, 'Stud2':75}
s1= pd.Series(d1)
print("Series from Dictionary\n", s1)
result = s1.apply(lambda x : 'EXCELLENT' if x>90 else 'WORK HARDER')
print(result)
** print(s1.apply(lambda y:y+y.sum()))
apply( pd.Series ).func( )
Functions / Methods of apply( ) -
1. stack ( )
import pandas as pd
nd= {'d1':{'Stud1':100, 'Stud2':95},
'd2':{'Stud3':95, 'Stud4':98}}
s1= pd.Series(nd)
print("Series from Dictionary (Original) ---\n", s1)
s = s1.apply(pd.Series).stack( )
print("\nThe stacked Series is ---\n", s)
Single dictionary series when stacked will return the same series as original
2. mathematical / statistical / aggregation function
s.apply(pd.Series).sum( )
s2 = s.apply(pd.Series).max()
print("\nApplied with func max() \n", s2)
Output -
Applied with func max()
0 100.0 dtype: float64
** These functions ( ) returns the value considering all the elements / values of the Series but we cannot have an output for desired individual row or column, otherwise the data should be introduced as dataframe.
10. type( series_object ) - to show the type of the series being passed and returns class type of the argument(object) passed as parameter
import pandas as pd
nd={'d1':{'Stud1':100, 'Stud2':95},
'd2':{'Stud3':95, 'Stud4':98}}
s1= pd.Series(nd)
print("Series from Dictionary")
print("The type of the Series is ", type(s1))
OUTPUT-
Series from Dictionary
The type of the Series is <class 'pandas.core.series.Series'>
import pandas as pd
nd={'d1':{'Stud1':100, 'Stud2':95},
'd2':{'Stud3':95, 'Stud4':98}}
s1= pd.Series(nd)
print("Series from Dictionary")
print("The type of the Series is ", type(s1))
s = s1.apply(pd.Series).stack()
print("One Series")
print("The type of nested series is", type(s))
print("The series converted to list is ", s.to_list())
print("The type of list is ", type(s))
OUTPUT -
Series from Dictionary The type of the Series is <class 'pandas.core.series.Series'> One Series The type of nested series is <class 'pandas.core.series.Series'> The series converted to list is [100.0, 95.0, 95.0, 98.0]




































No comments:
Post a Comment