Extracting an Element from a Series
A. Created from a Series of Scalar Value List - [100, 200, 300, 400, 100]
Series -
index address data
0 100
1 200
2 300
3 400
4 100
Case Default - extraction with the default index address
A. (Positional Positive Indexing)
# Accessing Elements through Positional Indexing on a Series created from Scalar Value List
import pandas
scalarvalue=[100,200,300,400,100]
print("The Scalar Value List is = ", scalarvalue)
S1=pandas.Series(scalarvalue)
# Positional indexing
print("The data at 1st index address is = ", S1[0])
The Scalar Value List is = [100, 200, 300, 400, 100] The data at '1st' row label thru positional index is = 100
Similarly,
S1[1] --> 200
S1[2] --> 300
.
.
S1[6]) --> IndexError: index 6 is out of bounds for axis 0 with size 5
B. Positional negative indexing
import pandas
scalarvalue=[100,200,300,400,100]
print("The Scalar Value List is = ", scalarvalue)
S1=pandas.Series(scalarvalue)
# Positional indexing
print("The last data is = ", S1[-2])
The Scalar Value List is = [100, 200, 300, 400, 100]
KeyError: -2-2 is not in range** The elements of a Series created from a Scalar value list can not be extracted through negative positional indexing.
Case 1 - When the row label index has been reindexed with non-numeric (character / String) value
A. Labelled Indexing
import pandas
scalarvalue=[100,200,300,400,100]
print("The Scalar Value List is = ", scalarvalue)
S1=pandas.Series(scalarvalue, index=['1st', '2nd', '3rd', '4th','5th'])
OR
S1=pandas.Series(scalarvalue, index=pandas.Index( ['1st', '2nd', '3rd', '4th','5th']) )
# Labelled indexing (non-numeric)
print("The data at '1st' row label thru labelled index is = ", S1['1st'])
The Scalar Value List is = [100, 200, 300, 400, 100] The data at '1st' row label thru labelled index is = 100
S1['2nd']) -- > 200 Labelled indexing (non-numeric)S1['3rd'] --> 300 Labelled indexing (non-numeric)** The elements of a Series created from a Scalar value list is when redefined with non-numeric row label indexing, then it's data can be extracted through the the labelled indexing
B. Positional Positive Indexing
# Accessing Elements through Positional Indexing of a Series created from Scalar Value List where the default index address has been redefined.
import pandas
scalarvalue=[100,200,300,400,100]
print("The Scalar Value List is = ", scalarvalue)
S1=pandas.Series(scalarvalue, index=['1st', '2nd', '3rd', '4th','5th'])
# Positional positive indexing (default)
print("The data at '1st' row label thru positional index is = ", S1[0])
The Scalar Value List is = [100, 200, 300, 400, 100] The data at '1st' row label thru labelled index is = 100 The data at '1st' row label thru positional index is = 100
S1[1] -- > 200 Positional indexing (default)S1[2] --> 300 Positional indexing (default)**The elements of a Series created from a Scalar value list is when redefined withnon-numeric row label indexing, then it's data can be extracted both through thepositional indexing and through the labelled indexing.Negative Positional indexingEx. 1 --import pandasscalarvalue=[100,200,300,400,100]print("The Scalar Value List is = ", scalarvalue)S1=pandas.Series(scalarvalue, index=['1st', '2nd', '3rd', '4th','5th'])# Positional indexingprint("The last data is = ", S1[-1])** The negative positional indexing can be used to extract an element from the Series created with non-numeric index.Ex. 2 -- Negative Positional indexingimport pandas scalarvalue=[100,200,300,400,100] print("The Scalar Value List is = ", scalarvalue) S1=pandas.Series(scalarvalue, index=['1st', '2nd', '3rd', '4th','5th']) # Positional indexing print("The last data is = ", S1[-2])The Scalar Value List is = [100, 200, 300, 400, 100] The last data is = 400Ex. 3 --S1[-6]) IndexError: index -6 is out of bounds for axis 0 with size 5
Case 2 - When the row label index is redefined with numeric row-labels (index)
Ex. 1 --
# Accessing Elements through Indexing on a Series created from Scalar Value List with numeric labelled index (other than positional indexing)
import pandas
scalarvalue=[100,200,300,400,100]
print("The Scalar Value List is = ", scalarvalue)
S1=pandas.Series(scalarvalue, index=[10, 20, 30, 40, 50])
# Labelled indexing
print("The data at '1st' row label thru labelled index is = ", S1[10])
# Positional indexing
print("The data at '1st' row label thru positional index is = ", S1[0])
The Scalar Value List is = [100, 200, 300, 400, 100] The data at '1st' row label thru labelled index is = 100
KeyError: 0Negative indexing
import pandasscalarvalue=[100,200,300,400,100]print("The Scalar Value List is = ", scalarvalue)S1=pandas.Series(scalarvalue, index=[10, 20, 30, 40, 50])# Negative Positional indexingprint("The data at '1st' row label thru positional index is = ", S1[-2])KeyError: -2
Ex. 2 --
# Accessing Elements Through Indexing on a Series created from Scalar Value List with numeric labelled index (other than positional indexing) import pandas scalarvalue=[100,200,300,400,100] print("The Scalar Value List is = ", scalarvalue) S1=pandas.Series(scalarvalue, index=[1,2,3,4,5]) # Labelled indexing print("The data at '1st' row label thru labelled index is = ", S1[5]) # Positional indexing print("The data at '1st' row label thru positional index is = ", S1[0])
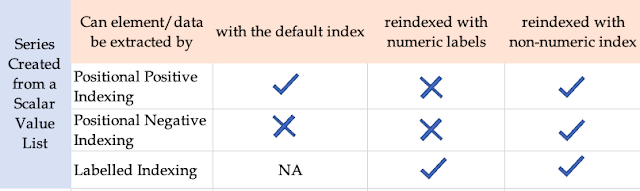
The Scalar Value List is = [100, 200, 300, 400, 100] The data at '1st' row label thru labelled index is = 100KeyError: 0# Positional Negative indexing print("The data at '1st' row label thru positional index is = ", S1[-1])KeyError: -1Summary Table - Series (Scalar Value List) Indexing (Extraction)***********************************************************************
No comments:
Post a Comment